Jacobian-Free Newton Krylov (JFNK) solver for the nonlinear ice-sheet/shelf momentum equations. More...
#include <JFNKSolver.H>
Classes | |
| class | Configuration |
Public Member Functions | |
| void | parseConfiguration (const char *a_prefix) |
| allows the usual configuration ("JFNKSolver.*") to be over-ridden More... | |
| const Configuration & | configuration () |
| allow read access to configuration entries More... | |
| Configuration & | get_evil_configuration () |
| allow write access to configuration entries More... | |
| virtual | ~JFNKSolver () |
| virtual JFNKSolver() int | solve (Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_horizontalVel, Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_calvedIce, Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_addedIce, Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_removedIce, Real &a_initialResidualNorm, Real &a_finalResidualNorm, const Real a_convergenceMetric, const Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_rhs, const Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_C, const Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_C0, const Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_A, const Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_muCoef, Vector< RefCountedPtr< LevelSigmaCS > > &a_coordSys, Real a_time, int a_lbase, int a_maxLevel) |
| Compute the horizontal, cell centered ice velocity ( u(x,y), v(x,y) ) [VERTICALLY INTEGRATED MODELS!]. More... | |
| virtual int | solve (Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_horizontalVel, Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_calvedIce, Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_addedIce, Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_removedIce, Real &a_initialResidualNorm, Real &a_finalResidualNorm, const Real a_convergenceMetric, const bool a_linear, const Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_rhs, const Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_C, const Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_C0, const Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_A, const Vector< LevelData< FArrayBox > * > &a_muCoef, Vector< RefCountedPtr< LevelSigmaCS > > &a_coordSys, Real a_time, int a_lbase, int a_maxLevel) |
| Uses a quasi-Newton method to solve a non-linear viscous tensor equation. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from IceVelocitySolver Public Member Functions inherited from IceVelocitySolver | |
| IceVelocitySolver () | |
| virtual | ~IceVelocitySolver () |
| virtual void | define (const ProblemDomain &a_coarseDomain, ConstitutiveRelation *a_constRel, BasalFrictionRelation *a_FrictionRel, const Vector< DisjointBoxLayout > &a_vectGrids, const Vector< int > &a_vectRefRatio, const RealVect &a_dxCrse, IceThicknessIBC *a_bc, int a_numLevels)=0 |
| (Re-)define IceVelocitySolver object for a given mesh and set of physics rules More... | |
| virtual void | setVerbosity (int a_verbosity) |
| virtual void | setMaxIterations (int a_max_iter) |
| if relevant, set max number of solver iterations More... | |
| virtual void | setTolerance (Real a_tolerance) |
| if relevant, set solver tolerance More... | |
| virtual bool | isDefined () |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from IceVelocitySolver Protected Attributes inherited from IceVelocitySolver | |
| bool | m_isDefined |
| int | m_verbosity |
Detailed Description
Jacobian-Free Newton Krylov (JFNK) solver for the nonlinear ice-sheet/shelf momentum equations.
The non-linear equation to be solved is L[u] u = r. L[u] is the viscous tensor operator whose coefficients depend on u.
Newton's method requires us to solve the linear system J[u] v = f = r - L[u] u, set u <- u + v, and repeat. Rather than write down the Jacobian, J, diretly, JFNK methods exploit a feature of Krylov sub-space projection iterative linear solvers: J is never needed, just matrix-vector products Jw for arbirrary w. This can be approximated by the finite difference formula ![$ J[u] w \approx (L[u + hw](u + hw) - L u)/h $](form_101.png) .
.
However, Krylov methods don't perform well without a preconditioner. The preconditioner here involves solutions of the linear viscous tensor equation L[u] q = r, and depends on the methods available to solve that ,and the assumption that L and J have approximately the same major eigenvectors
Since Newton's method can converge slowly, or not at all, when the initial guess far from the solution, our first few iterations do not use the finite difference formula: they simply approximate J[u] with L[u]. This is usually called a Picard method, and although it is outperformed by JFNK close to the solution, elsewhere it is the better choice because (a) L[u]v = f is easier to solve than J[u]v = f (since the preconditioner is perfect in that case) and (b) JFNK leads to re-calculation of the viscosity at every 'inner' Kyrlov iteration , whereas Picard only requires re-calculation of the viscosity at every 'outer' Newton iteration.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ ~JFNKSolver()
|
inlinevirtual |
References LinearizedVTOp::JFNKSolver.
Member Function Documentation
◆ configuration()
|
inline |
allow read access to configuration entries
◆ get_evil_configuration()
|
inline |
allow write access to configuration entries
- Todo:
- get rid of this
References IceUtility::eliminateFastIce().
Referenced by InverseVerticallyIntegratedVelocitySolver::nDoF().
◆ parseConfiguration()
|
inline |
allows the usual configuration ("JFNKSolver.*") to be over-ridden
References JFNKSolver::Configuration::parse().
◆ solve() [1/2]
|
inlinevirtual |
Compute the horizontal, cell centered ice velocity ( u(x,y), v(x,y) ) [VERTICALLY INTEGRATED MODELS!].
- Parameters
-
a_horizontalVel on input an initial guess ( u_0(x,y), v_0(x,y) ), on output ( u(x,y), v(x,y) ) a_initialResidualNorm residual norm given the initial guess a_finalResidualNorm residual norm at the end of the calculation a_convergenceMetric desired a_finalResidualNorm/a_initialResidualNorm a_rhs right hand side of the stress balance equation: the driving stress (x,y) components a_C main basal friction coefficient : 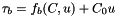
a_C0 auxilliary basal friction coefficient : 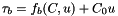
a_A flow rate factor: one component per layer a_muCoef stiffness factor: one component a_coordSys ice sheet geoemtry a_time current time a_lbase lowest mesh level (probably doesn't work!) a_maxLevel highest mesh level
- Returns
- 0 if solver converges successfully
Implements IceVelocitySolver.
References IceUtility::defineRHS(), and IceUtility::eliminateFastIce().
Referenced by InverseVerticallyIntegratedVelocitySolver::nDoF(), PetscIceSolver::solve(), and AmrIce::solveVelocityField().
◆ solve() [2/2]
|
virtual |
Uses a quasi-Newton method to solve a non-linear viscous tensor equation.
The equation to be solved is L[u] u = r, where r is input in a_rhs, L[u] a the viscous tensor operator whose coefficients depend on u. a_u is an initial guess for u on input, and contains the result (u) on output
if a_linear == true, then the equation is L[u*] u = r, where u* is the input a_u, and u is the output. This option is useful for solving e.g the adjoint equation.
scale u (e.g if u is in m/s, scaling to m/a)
References NonlinearViscousTensor::alpha(), LinearizedVTOp::create(), LinearizedVTOp::current(), CGSolver< T >::define(), IceUtility::eliminateFastIce(), LinearizedVTOp::incr(), JFNK_LINEARIZATION_MODE, NonlinearViscousTensor::lambda(), CGSolver< T >::m_eps, CGSolver< T >::m_hang, CGSolver< T >::m_imax, CGSolver< T >::m_normType, CGSolver< T >::m_numRestarts, CGSolver< T >::m_verbosity, NonlinearViscousTensor::mu(), LinearizedVTOp::norm(), LinearizedVTOp::outerResidual(), LinearizedVTOp::PetscAMRSolver, PICARD_LINEARIZATION_MODE, LinearizedVTOp::residual(), IceNonlinearViscousTensor::setFaceViscCoef(), NonlinearViscousTensor::setState(), IceNonlinearViscousTensor::setState(), and LinearizedVTOp::setToZero().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
 1.8.13
1.8.13