#include <BaseFab.H>
Inheritance diagram for BaseFab< T >:

Public Methods | |
| BaseFab () | |
| {\bf constructors, destructor and defines} | |
| BaseFab (const Box &a_bx, int a_n, T *a_alias=NULL) | |
| BaseFab (const Interval &a_comps, BaseFab< T > &a_original) | |
| virtual | ~BaseFab () |
| void | resize (const Box &a_b, int a_n=1, T *a_alias=NULL) |
| virtual void | define (const Box &a_box, int a_comps, T *a_alias=NULL) |
| virtual void | define (const Interval &a_comps, BaseFab< T > &a_original) |
| void | clear () |
| int | nComp () const |
| {\bf accessors} | |
| const Box & | box () const |
| const int * | size () const |
| const IntVect & | smallEnd () const |
| const IntVect & | bigEnd () const |
| Interval | interval () const |
| T & | operator() (const IntVect &a_p, int a_N) |
| T & | operator() (const IntVect &a_p) |
| const T & | operator() (const IntVect &p, int N) const |
| const T & | operator() (const IntVect &p) const |
| void | getVal (T *a_data, const IntVect &a_pos, int a_N, int a_numcomp) const |
| void | getVal (T *a_data, const IntVect &a_pos) const |
| const int * | loVect () const |
| {\bf Fortran interface functions} | |
| const int * | hiVect () const |
| const int * | nCompPtr () const |
| T * | dataPtr (int a_n=0) |
| const T * | dataPtr (int a_n=0) const |
| bool | contains (const BaseFab< T > &a_fab) const |
| {\bf comparison functions} | |
| bool | contains (const Box &a_bx) const |
| void | setVal (T a_x, const Box &a_bx, int a_nstart, int a_numcomp) |
| {\bf data modification functions} | |
| void | setVal (T a_x, const Box &a_bx, int a_n) |
| void | setVal (T a_x, int a_n) |
| void | setVal (T a_x) |
| BaseFab< T > & | copy (const BaseFab< T > &a_src, const Box &a_srcbox, int a_srccomp, const Box &a_destbox, int a_destcomp, int a_numcomp) |
| BaseFab< T > & | copy (const BaseFab< T > &a_src, int a_srccomp, int a_destcomp, int a_numcomp=1) |
| BaseFab< T > & | copy (const BaseFab< T > &a_src, const Box &a_destbox) |
| BaseFab< T > & | copy (const BaseFab< T > &a_src) |
| void | copy (const Box &a_RegionFrom, const Interval &a_Cdest, const Box &a_RegionTo, const BaseFab< T > &a_src, const Interval &a_Csrc) |
| BaseFab< T > & | shift (const IntVect &a_v) |
| {\bf domain modification functions} | |
| BaseFab< T > & | shift (int a_idir, int a_ncells) |
| BaseFab< T > & | shiftHalf (int a_dir, int a_numHalfs) |
| BaseFab< T > & | shiftHalf (const IntVect &a_v) |
| virtual int | size (const Box &a_box, const Interval &a_comps) const |
| {\bf linearization functions} | |
| virtual void | linearOut (void *a_buf, const Box &a_R, const Interval &a_comps) const |
| virtual void | linearIn (void *a_buf, const Box &a_R, const Interval &a_comps) |
Static Public Methods | |
| int | preAllocatable () |
Protected Methods | |
| void | define () |
| void | undefine () |
| virtual void | performCopy (const BaseFab< T > &a_src, const Box &a_srcbox, int a_srccomp, const Box &a_destbox, int a_destcomp, int a_numcomp) |
| void | performSetVal (T a_x, const Box &a_bx, int a_nstart, int a_numcomp) |
Static Protected Methods | |
| std::string | name () |
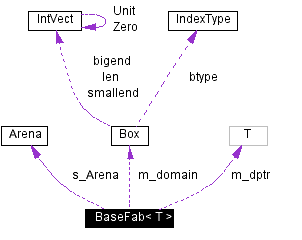
Protected Attributes | |
| Box | m_domain |
| int | m_nvar |
| long | m_numpts |
| long | m_truesize |
| T * | m_dptr |
| bool | m_aliased |
Static Protected Attributes | |
| Arena * | s_Arena = NULL |
|
|||||||||
|
{\bf constructors, destructor and defines} Constructs an invalid `BaseFab'. The domain is invalid, the number of components is zero, and no actual array memory is allocated. An invalid `BaseFab' must be resize()d (see `BaseFab::resize') before use. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Constructs a BaseFab with desired domain and number of components. |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Constructs an 'aliased' BaseFab of the requested interval of the argument BaseFab. This BaseFab does not allocate any memory, but sets its data pointer into the memory pointed to by the argument BaseFab. It is the users responsiblity to ensure this aliased BaseFab is not used after the original BaseFab has deleted its data ptr (resize, define(..) called, or destruction, etc.). This aliased BaseFab will also generate side effects (modifying the values of data in one will modify the other's data). This aliased BaseFab will have a_comps.size() components, starting at zero. |
|
|||||||||
|
The destructor deletes the array memory. Unless this was an aliased BaseFab. |
|
|||||||||
|
Returns the upper corner of the domain. See class `Box' for analogue. |
|
|||||||||
|
Returns the domain (box) where the array is defined. |
|
|||||||||
|
The function returns the `BaseFab' to the invalid state. (See comments for constructors above.) The memory is freed. Reimplemented in BinFab< T >. |
|
||||||||||
|
Returns true if a_bx is totally contained within the domain of this `BaseFab'. |
|
||||||||||
|
{\bf comparison functions} Returns true if the domain of a_fab is totally contained within the domain of this `BaseFab'. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Copy from a subsection of one box into another. Assumes the boxes are both in the same index space, and that box R is completely contained in both the source and destination boxes. |
|
||||||||||
|
Modifies this BaseFab by coping the contents of the argument BaseFab into it. A copy within the intersecting region of the domains of the two BaseFabs is performed. All components are copied. |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Modifies this BaseFab by coping the contents of the argument BaseFab into it. A copy within the intersecting region of the domains of the two BaseFabs and the specified Box a_destbox is performed. All components are copied. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Modifies this BaseFab by copying the contents of the argument BaseFab into it. A copy within the intersecting region of the domains of the two BaseFabs is performed. The user specifies how many components are copied, starting at component a_srccomp in a_src and stored starting at component a_destcomp. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Modifies this BaseFab by copying the contents of the argument BaseFab into it. This, the most general form of copy, specifies the contents of any sub-box a_srcbox in `BaseFab' a_src may be copied into a (possibly different) a_destbox in the destination `BaseFab'. Note that although the a_srcbox and the a_destbox may be disjoint, they must be the same size and shape. If the sizes differ, the copy is undefined and a runtime error results. This copy function is the only one of the copy functions to allow a copy between differing boxes. The user also specifies how many components are copied, starting at component a_srccomp in a_src and stored starting at component a_destcomp. The results are UNDEFINED if the a_src and dest BaseFabs are the same and the a_srcbox and a_destbox overlap. |
|
||||||||||
|
Returns a constant pointer to an object of type T that is the value of the a_nth component associated with the cell at the low end of the domain. This is commonly used to get a pointer to data in the array which is then handed off to a Fortran subroutine. It should not be used in any other context!!! Remember that data is stored in Fortran array order, with the component index coming last. In other words, `dataPtr' returns a pointer to all the a_nth components. |
|
||||||||||
|
Returns a pointer to an object of type T that is the value of the a_nth component associated with the cell at the low end of the domain. This is commonly used to get a pointer to data in the array which is then handed off to a Fortran subroutine. It should not be used in any other context!!! Remember that data is stored in Fortran array order, with the component index coming last. In other words, `dataPtr' returns a pointer to all the a_nth components. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
alias define. no memory allocated. this BaseFab sets its data ptr directly in the a_original BaseFab data. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Make BaseFab with desired domain and number of components. Existing data is lost. Data is in uninialized state. Reimplemented in FArrayBox. |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
This function puts all component values, starting at component 0, from position pos in the domain into array data, that must be allocated by the user. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This function puts numcomp component values, starting at component N, from position pos in the domain into array data, that must be allocated by the user. |
|
|||||||||
|
Returns the upper corner of the domain. Instead of returning them in the form of IntVects, as in smallEnd and bigEnd, it returns the values as a pointer to an array of constant integers. This is useful when interfacing to Fortran subroutines. It should not be used in any other context!!! |
|
|||||||||
|
Returns an Interval for the entire range on components. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Reimplemented in BinFab< T >. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Write a linear representation of the internal data. Assumes that sufficient memory for the buffer has already been allocated by the caller. Reimplemented in BinFab< T >. |
|
|||||||||
|
{\bf Fortran interface functions} Returns the lower corner of the domain. Instead of returning them in the form of IntVects, as in smallEnd and bigEnd, it returns the values as a pointer to an array of constant integers. This is useful when interfacing to Fortran subroutines. It should not be used in any other context!!! |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
{\bf accessors} Returns the number of components. |
|
|||||||||
|
Returns a pointer to an integer that contains the number of components in the BaseFab. This is useful when interfacing to Fortran subroutines. It should not be used in any other context!!! |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Returns a conatant reference to the Nth component value defined at position p in the domain. This operator may be inefficient if the C++ compiler is unable to optimize the C++ code. |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Returns a modifiable lvalue reference to the Nth component value defined at position p in the domain. This operator may be inefficient if the C++ compiler is unable to optimize the C++ code. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Reimplemented in FArrayBox. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
Reimplemented in BinFab< T >. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
This function resizes a `BaseFab' so it covers the `Box' a_b with a_n components. The default action is that under resize()ing, the memory allocated for the `BaseFab' only grows and never shrinks. This function is particularly useful when a `BaseFab' is used as a temporary space which must be a different size whenever it is used. Resize()ing a temp will often be faster than re-allocating a `BaseFab' because memory allocation can often be avoided. |
|
||||||||||
|
Modifies this BaseFab so that all values of all components are set to the given value, a_x. |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Modifies this BaseFab so that all values of a component, a_n, are set to the given value, a_x. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Modifies this BaseFab so that all values of a component, a_n, in the specified Box, a_bx, are set to the given value, a_x. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
{\bf data modification functions} The setVal functions set subregions in the `BaseFab' to a constant value. This most general form specifies the subbox, the starting component number, and the number of components to be set. |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Modifies the domain of this BaseFab by shifting it a_ncells indexing positions in coordinate direction a_idir. Directions are zero-based. It is an error if not 0 <= a_idir < SpaceDim. There is no effect upon the array memory. |
|
||||||||||
|
{\bf domain modification functions} Modifies the domain of this BaseFab by shifting. Equivalent to fab.shift(0,a_v[0]).shift(1,a_v[1])... There is no effect upon the array memory. |
|
||||||||||
|
Modifies the domain of this BaseFab by shifting by half indices. Equivalent to fab.shiftHalf(0,a_v[0]).shiftHalf(1,a_v[1]) ... There is no effect upon the array memory. |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Modifies the domain of this BaseFab by shifting by "half" indices, thereby converting the Box from type CELL to NODE or vice-versa. fab.shiftHalf(0,1) shifts the domain to the right by 1/2 cells. fab.shiftHalf(1,-3) shifts the domain in the -j direction by 3/2 cells. NOTE: If a_numHalfs is EVEN the shift is a_numHalfs/2 full zones and hence will not change the type. This is: fab.shiftHalf(1,4) == fab.shift(1,2). Directions are zero-based. It is an error if not 0 <= a_dir < SpaceDim. There is no effect upon the array memory. |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
{\bf linearization functions} Returns the size, in number of bytes, of a flat linear representation of the data in this object in the area defined by the input Box a_box and the component Interval a_comps. The size does not include the size of a_box and a_comps. Reimplemented in BinFab< T >. |
|
|||||||||
|
Returns a pointer to an array of SpaceDim integers giving the length of the domain in each direction. Reimplemented in BinFab< T >. |
|
|||||||||
|
Returns the lower corner of the domain. See class `Box' for analogue. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
 1.2.16
1.2.16